The Rydberg Equation calculator computes the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation based on two energy state and the Rydberg constant.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (n2) Principal Quantum Number of Higher Energy Level
- (n1) Principal Quantum Number of Lower Energy Level
Wavelength (λ): The wavelength is returned in nanometers. However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
This equation, the Rydberg Equation, computes the wavelengths corresponding to the hydrogen atom's energy level differences. These differences between energy levels is equal to the energy emitted or absorbed as photons when an electron transitions between two of the quantum energy levels.
The input to this equation are:
- n2 = the integer number of the higher energy state for a spectral emission
- n1 = the integer number of the lower energy state for a spectral emission
*n1=1 is the lowest energy level
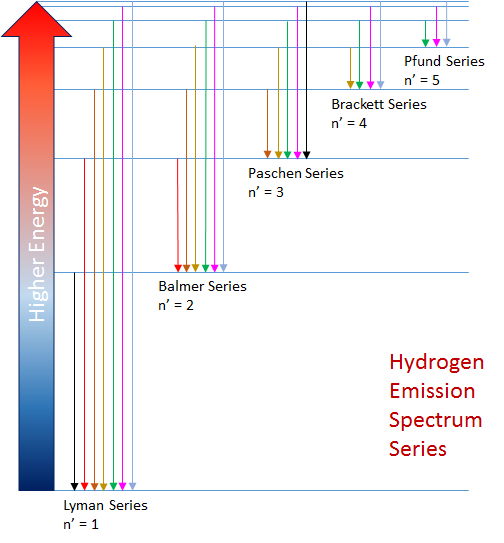
The wavelength computed in this Rydberg Equation is reported in units of nanometers (nm). In the following graphic n2 is shown as n and n1 is shown as n`.
Notes
The emission spectrum for the transitions between all the energy levels of the hydrogen atom can be partitioned into groups of transitions or spectral series, where the lower energy state in any transition, n', characterizes the spectral series. The energy states, created by the electromagnetic forces between electrons and protons in the atom, are fixed. This ensures the hydrogen spectrum is always emitted at the precise wavelengths defined by the Rydberg Equation. The graphics shows the first five of an infinite number of spectral series for the hydrogen atom.
One of the uses of these fixed and well-defined spectral series is in the astronomical detection of hydrogen from the emissions of distant stars.